Early STD Testing: Why Timely Detection Matters for Your Health
When it comes to sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), early detection and treatment are crucial for
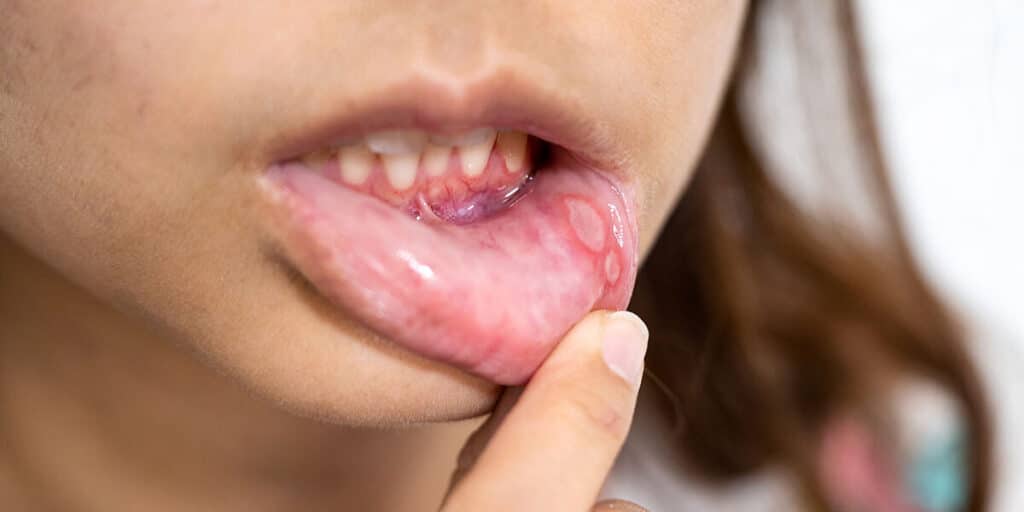
Sores in and around the mouth have a variety of causes: injuries, nutritional deficiencies, medication side effects, and even STD symptoms. While you may think you have a canker sore, you may not know what caused it or whether you can spread it to others — sexually or otherwise.
If you are not sure whether a sexually transmitted disease (STD) is causing your mouth sores, a rapid STD test can let you know in just 24 to 48 hours. In the meantime, Rapid STD Testing answers the question, “Are canker sores an STD?” We also cover what triggers canker sores, the risk factors in their development, how long they usually last, and how you can prevent and treat them.
Both STDs and canker sores can result in oral lesions that are often painful. However, there are many differences between the two conditions, including what causes them.
Canker sores are small, round ulcers that develop in the soft tissues of the mouth. Common locations include the inner cheeks and lips, the tongue, gums, and back of the throat. Typically white with a red border, canker sores can cause pain for several days.
Several STDs can cause sores in the mouth. If you’re wondering, “How can I tell the difference between a canker sore and an STD-related oral sore?” we’ll go over how STD sores and canker sores are different.
Like canker sores, cold sores are small, painful mouth lesions. Unlike canker sores, cold sores form as blisters on the outside of the lips rather than as ulcers inside the mouth. In addition, cold sores are the result of the herpes simplex virus (HSV-1 or HSV-2).
You can contract the herpes virus through sexual activity, non-sexual contact such as kissing, or sharing infected objects (like razors or utensils). Although antiviral medications can help prevent herpes outbreaks, the virus stays in your body forever.
Syphilis, a sexually transmitted bacterial infection, can also cause round oral sores. These lesions (called chancres) tend to be painless, unlike canker sores. While chancres most often appear on the genitals, they can also appear on the mouth, lips, tongue, and tonsils. Since chancres don’t cause pain, they often go unnoticed. They clear up with antibiotic treatment.
The result of a sexually transmitted bacteria called Haemophilus ducreyi, chancroid causes painful sores in the throat or on the genitals. Chancroid is rare in the United States.
Unlike syphilis and chancroid, canker sores are non-contagious mouth sores. It is not clear exactly what causes canker sores, but you cannot transmit them through sexual activity.
Because both STDs and canker sores can affect your mouth, many people wonder, “Are canker sores an STD?” The truth is that canker sores are not STDs. Here are other common misconceptions about them.
While the exact causes of canker sores are unknown, scientists and doctors have identified several risk factors and likely triggers.
Canker sore causes include the following:
Some people are more likely to develop canker sores based on factors such as the following:
Because canker sores often run in families, researchers believe there might be a hereditary component. As many as 40% of patients have a family history of canker sores (called aphthous ulcers in medical terminology). People who carry certain genetic variants involved in pro-inflammatory responses are more likely to develop canker sores earlier and more severely.
One of the more painful conditions relating to ulcers of the mouth is called recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS). Present in around 5% to 20% of the general population, RAS causes recurrent episodes of shallow, painful sores every few months or even every few days. Studies have shown that genetic factors play a crucial role in the development of RAS.
Canker sores do not come from poor oral hygiene habits. However, poor oral health can exacerbate your condition. For example, food particles or residue in your mouth may trigger or worsen a canker sore.
While it may be uncomfortable to brush your teeth when you have a sore, it is important to maintain good oral health and hygiene by brushing your teeth with a soft-bristled brush twice a day, flossing at least once a day, and drinking plenty of water.
Most simple canker sores heal on their own within one to two weeks without any treatment. If you have complex or major canker sores, they may take up to four weeks to heal and may leave a scar in the mucous membrane.
Canker sore treatments depend on the underlying causes and symptom severity. Some common treatments include:
In minor cases, over-the-counter medications can help relieve pain and promote healing. In severe or recurrent cases, prescription medications can reduce inflammation and aid healing.
If you’re looking for the best way to treat canker sores at home, know that at-home treatments cannot instantly heal mouth ulcers. However, the following remedies may help manage the pain and promote healing:
Everyone is different, but most people develop canker sores three to six times a year. Changes in diet or lifestyle can reduce the frequency of canker sores. While completely preventing canker sores is not possible, you can take the following steps to lower your risk.
While most canker sores heal on their own, you should seek professional medical advice in the following situations:
We hope we have answered the question, “Are canker sores an STD?” To recap, canker sores are not contagious, and you cannot transmit them sexually. However, if you’re unsure what kind of mouth sore you have, it’s important to get tested.
At Rapid STD Testing, we offer quick and confidential STD testing in all 50 states, making it easy to find a sexual health clinic near you. For a single STD test or a comprehensive 10-panel STD test, call us today or input your zip code to find a local testing center.

No embarrassing exams, long waiting lines, or multiple visits. Just a quick lab visit for fast results.
Discover a lifestyle-focused approach to quality content at RapidSTDtesting.com. Unlike others, we don't rely on gimmicks or fabricated data to lure visitors. Our commitment goes beyond clicks – we're dedicated to answering the questions you search for online. With a team comprising medical experts and content specialists, our articles are meticulously crafted to promote STD testing, educate, and dismantle social stigmas.
Embrace a confidential atmosphere with our private testing options, ensuring your privacy is paramount. Every article is meticulously fact-checked and approved by medical advisors, guaranteeing accuracy and reliability. Our team, comprised of doctors and medical professionals, ensures that each piece of content serves a purpose – to inform, educate, and promote awareness.
Join us as we bridge the gap between medical expertise and lifestyle choices. RapidSTDtesting.com is your trusted source for informative, medically vetted content.